Random forests or decision tree forests focuses only on ensembles of decision trees. This method combines the base principles of bagging with random feature selection to add additional diversity to the decision tree models. After the ensemble of trees (the forest) is generated, the model uses a vote to combine the trees’ predictions.
As the ensembles uses only a small, random portion of the full feature set, random forests can handle extremely large datasets, where the so-called “curse of dimensionality” might cause other models to fail. At the same time, its error rates for most learning tasks are on par with nearly any other method.
It is a all purpose model that performs well in most problems, but unlike a decision tree, the model is not easily interpretable. Can handle noisy, missing data as well as categorical or continuous features, but selects only the most important features.
Here we will work with the Pima Indians Diabetes database to predict the onset of diabetes based on diagnostic measures: https://www.kaggle.com/hconner2/diabetes/data
Attributes:
Pregnancies: Number of times pregnant
Glucose: Plasma glucose concentration a 2 hours in an oral glucose tolerance test
BloodPressure: Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg)
SkinThickness: Triceps skin fold thickness (mm)
Insulin: 2-Hour serum insulin (mu U/ml)
BMI: Body mass index (weight in kg/(height in m)^2)
DiabetesPedigreeFunction: Diabetes pedigree function
Age: Age (years)
Outcome: Class variable (0 or 1)
Step 1. Collecting data. Exploring and preparing the data.
diabetes = read.csv("C:/Users/ester/Desktop/BLOG/diabetes.csv", sep = "," , dec = ".", header = TRUE)
head(diabetes)## Pregnancies Glucose BloodPressure SkinThickness Insulin BMI
## 1 6 148 72 35 0 33.6
## 2 1 85 66 29 0 26.6
## 3 8 183 64 0 0 23.3
## 4 1 89 66 23 94 28.1
## 5 0 137 40 35 168 43.1
## 6 5 116 74 0 0 25.6
## DiabetesPedigreeFunction Age Outcome
## 1 0.627 50 1
## 2 0.351 31 0
## 3 0.672 32 1
## 4 0.167 21 0
## 5 2.288 33 1
## 6 0.201 30 0summary(diabetes)## Pregnancies Glucose BloodPressure SkinThickness
## Min. : 0.000 Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0.00
## 1st Qu.: 1.000 1st Qu.: 99.0 1st Qu.: 62.00 1st Qu.: 0.00
## Median : 3.000 Median :117.0 Median : 72.00 Median :23.00
## Mean : 3.845 Mean :120.9 Mean : 69.11 Mean :20.54
## 3rd Qu.: 6.000 3rd Qu.:140.2 3rd Qu.: 80.00 3rd Qu.:32.00
## Max. :17.000 Max. :199.0 Max. :122.00 Max. :99.00
## Insulin BMI DiabetesPedigreeFunction Age
## Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0.00 Min. :0.0780 Min. :21.00
## 1st Qu.: 0.0 1st Qu.:27.30 1st Qu.:0.2437 1st Qu.:24.00
## Median : 30.5 Median :32.00 Median :0.3725 Median :29.00
## Mean : 79.8 Mean :31.99 Mean :0.4719 Mean :33.24
## 3rd Qu.:127.2 3rd Qu.:36.60 3rd Qu.:0.6262 3rd Qu.:41.00
## Max. :846.0 Max. :67.10 Max. :2.4200 Max. :81.00
## Outcome
## Min. :0.000
## 1st Qu.:0.000
## Median :0.000
## Mean :0.349
## 3rd Qu.:1.000
## Max. :1.000str(diabetes)## 'data.frame': 768 obs. of 9 variables:
## $ Pregnancies : int 6 1 8 1 0 5 3 10 2 8 ...
## $ Glucose : int 148 85 183 89 137 116 78 115 197 125 ...
## $ BloodPressure : int 72 66 64 66 40 74 50 0 70 96 ...
## $ SkinThickness : int 35 29 0 23 35 0 32 0 45 0 ...
## $ Insulin : int 0 0 0 94 168 0 88 0 543 0 ...
## $ BMI : num 33.6 26.6 23.3 28.1 43.1 25.6 31 35.3 30.5 0 ...
## $ DiabetesPedigreeFunction: num 0.627 0.351 0.672 0.167 2.288 ...
## $ Age : int 50 31 32 21 33 30 26 29 53 54 ...
## $ Outcome : int 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 ...
Here, we have to be careful about how the data has been coded. First, we see that the
Outcome is numeric while it should be categorical:diabetes$Outcome = factor(diabetes$Outcome)
summary(diabetes$Outcome)## 0 1
## 500 268levels(diabetes$Outcome) = c('negative', 'positive')
Secondly, we see that in many variables there are zeros that do not make sense, for example,
BloodPressure, BMI, etc. We can assume that the zeros represent the NA values and need to be recoded correctly:diabetes$Glucose[diabetes$Glucose == 0 ] = NA
diabetes$BloodPressure[diabetes$BloodPressure == 0 ] = NA
diabetes$SkinThickness[diabetes$SkinThickness == 0 ] = NA
diabetes$Insulin[diabetes$Insulin == 0 ] = NA
diabetes$BMI[diabetes$BMI == 0 ] = NA
diabetes = na.omit(diabetes)
summary(diabetes)## Pregnancies Glucose BloodPressure SkinThickness
## Min. : 0.000 Min. : 56.0 Min. : 24.00 Min. : 7.00
## 1st Qu.: 1.000 1st Qu.: 99.0 1st Qu.: 62.00 1st Qu.:21.00
## Median : 2.000 Median :119.0 Median : 70.00 Median :29.00
## Mean : 3.301 Mean :122.6 Mean : 70.66 Mean :29.15
## 3rd Qu.: 5.000 3rd Qu.:143.0 3rd Qu.: 78.00 3rd Qu.:37.00
## Max. :17.000 Max. :198.0 Max. :110.00 Max. :63.00
## Insulin BMI DiabetesPedigreeFunction Age
## Min. : 14.00 Min. :18.20 Min. :0.0850 Min. :21.00
## 1st Qu.: 76.75 1st Qu.:28.40 1st Qu.:0.2697 1st Qu.:23.00
## Median :125.50 Median :33.20 Median :0.4495 Median :27.00
## Mean :156.06 Mean :33.09 Mean :0.5230 Mean :30.86
## 3rd Qu.:190.00 3rd Qu.:37.10 3rd Qu.:0.6870 3rd Qu.:36.00
## Max. :846.00 Max. :67.10 Max. :2.4200 Max. :81.00
## Outcome
## negative:262
## positive:130
##
##
##
##
The data we are going to work with has a dimention of 392 rows and 9 columns.
Step 2. Creating training and testing datasets
We will divide our data into two different sets: a training dataset that will be used to build the model and a test dataset that will be used to estimate the predictive accuracy of the model.
The dataset will be divided into training (70%) and testing (30%) sets, we create the data sets using the
caret package:library(caret)set.seed(123)
train_ind= createDataPartition(y = diabetes$Outcome,p = 0.7,list = FALSE)
train = diabetes[train_ind,]
head(train)## Pregnancies Glucose BloodPressure SkinThickness Insulin BMI
## 4 1 89 66 23 94 28.1
## 5 0 137 40 35 168 43.1
## 14 1 189 60 23 846 30.1
## 15 5 166 72 19 175 25.8
## 19 1 103 30 38 83 43.3
## 20 1 115 70 30 96 34.6
## DiabetesPedigreeFunction Age Outcome
## 4 0.167 21 negative
## 5 2.288 33 positive
## 14 0.398 59 positive
## 15 0.587 51 positive
## 19 0.183 33 negative
## 20 0.529 32 positivetest = diabetes[-train_ind,]
head(test)## Pregnancies Glucose BloodPressure SkinThickness Insulin BMI
## 7 3 78 50 32 88 31.0
## 9 2 197 70 45 543 30.5
## 17 0 118 84 47 230 45.8
## 21 3 126 88 41 235 39.3
## 25 11 143 94 33 146 36.6
## 26 10 125 70 26 115 31.1
## DiabetesPedigreeFunction Age Outcome
## 7 0.248 26 positive
## 9 0.158 53 positive
## 17 0.551 31 positive
## 21 0.704 27 negative
## 25 0.254 51 positive
## 26 0.205 41 positive
The training set has 275 samples, and the testing set has 117 samples.
Step 3. Training a model on the data
We will use the function
randomForest in the package randomForest.
The function
radomForest has the following important parameters:
-
ntree:number of trees
-
mtry: Number of variables randomly sampled as candidates at each split. Note that the default values are different for classification (sqrt(p) where p is number of variables in x) and regression (p/3)#install.packages('randomForest')
library(randomForest)rf =randomForest(Outcome~., data = train, ntree= 50, mtry=sqrt(7))
rf##
## Call:
## randomForest(formula = Outcome ~ ., data = train, ntree = 50, mtry = sqrt(7))
## Type of random forest: classification
## Number of trees: 50
## No. of variables tried at each split: 3
##
## OOB estimate of error rate: 22.91%
## Confusion matrix:
## negative positive class.error
## negative 159 25 0.1358696
## positive 38 53 0.4175824plot(rf)Step 4. Evaluating model performance
predictions = predict(rf, test, type= "response")
head(predictions)## 7 9 17 21 25 26
## negative positive positive negative positive negative
## Levels: negative positivelibrary(caret)
confu1 =confusionMatrix(predictions, test$Outcome , positive = 'positive')
confu1## Confusion Matrix and Statistics
##
## Reference
## Prediction negative positive
## negative 68 15
## positive 10 24
##
## Accuracy : 0.7863
## 95% CI : (0.7009, 0.8567)
## No Information Rate : 0.6667
## P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 0.003138
##
## Kappa : 0.5033
## Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.423711
##
## Sensitivity : 0.6154
## Specificity : 0.8718
## Pos Pred Value : 0.7059
## Neg Pred Value : 0.8193
## Prevalence : 0.3333
## Detection Rate : 0.2051
## Detection Prevalence : 0.2906
## Balanced Accuracy : 0.7436
##
## 'Positive' Class : positive
##
The accuracy of the model is 78.63 %, whit an error rate of 21.37 %.
The kappa statistic of the model is 0.50331.
The sensitivity of the model is 0.61538,and the especificity of the model is 0.87179.
The precision of the model is 0.70588,and the recall of the model is 0.61538.
The value of the F-measure of the model is 0.6575.
Step 5. Improving model performance (ntree= 1000)
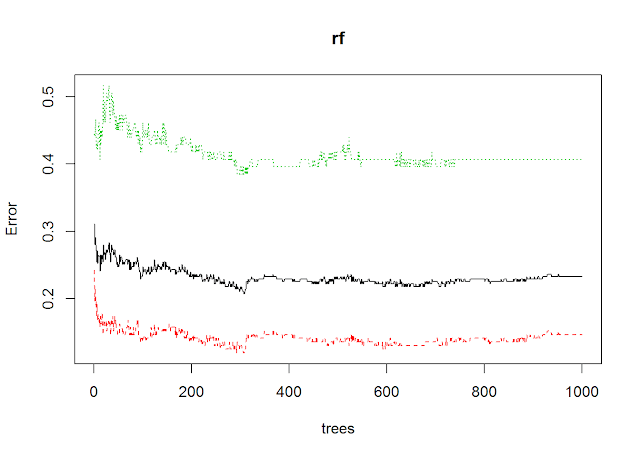
rf =randomForest(Outcome~., data = train, ntree= 1000, mtry=sqrt(7))
rf##
## Call:
## randomForest(formula = Outcome ~ ., data = train, ntree = 1000, mtry = sqrt(7))
## Type of random forest: classification
## Number of trees: 1000
## No. of variables tried at each split: 3
##
## OOB estimate of error rate: 23.27%
## Confusion matrix:
## negative positive class.error
## negative 157 27 0.1467391
## positive 37 54 0.4065934plot(rf)predictions =predict(rf, test, type= "response")
head(predictions)## 7 9 17 21 25 26
## negative positive positive negative positive negative
## Levels: negative positivelibrary(caret)
confu2 =confusionMatrix(predictions, test$Outcome , positive = 'positive')
confu2## Confusion Matrix and Statistics
##
## Reference
## Prediction negative positive
## negative 70 13
## positive 8 26
##
## Accuracy : 0.8205
## 95% CI : (0.7388, 0.8853)
## No Information Rate : 0.6667
## P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 0.0001599
##
## Kappa : 0.5828
## Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.3827331
##
## Sensitivity : 0.6667
## Specificity : 0.8974
## Pos Pred Value : 0.7647
## Neg Pred Value : 0.8434
## Prevalence : 0.3333
## Detection Rate : 0.2222
## Detection Prevalence : 0.2906
## Balanced Accuracy : 0.7821
##
## 'Positive' Class : positive
##
The accuracy of the model is 82.05%, whit an error rate of 17.95 %.
The kappa statistic of the model is 0.58278.
The sensitivity of the model is 0.66667,and the especificity of the model is 0.89744.
The precision of the model is 0.76471,and the recall of the model is 0.66667.
The value of the F-measure of the model is 0.7123.